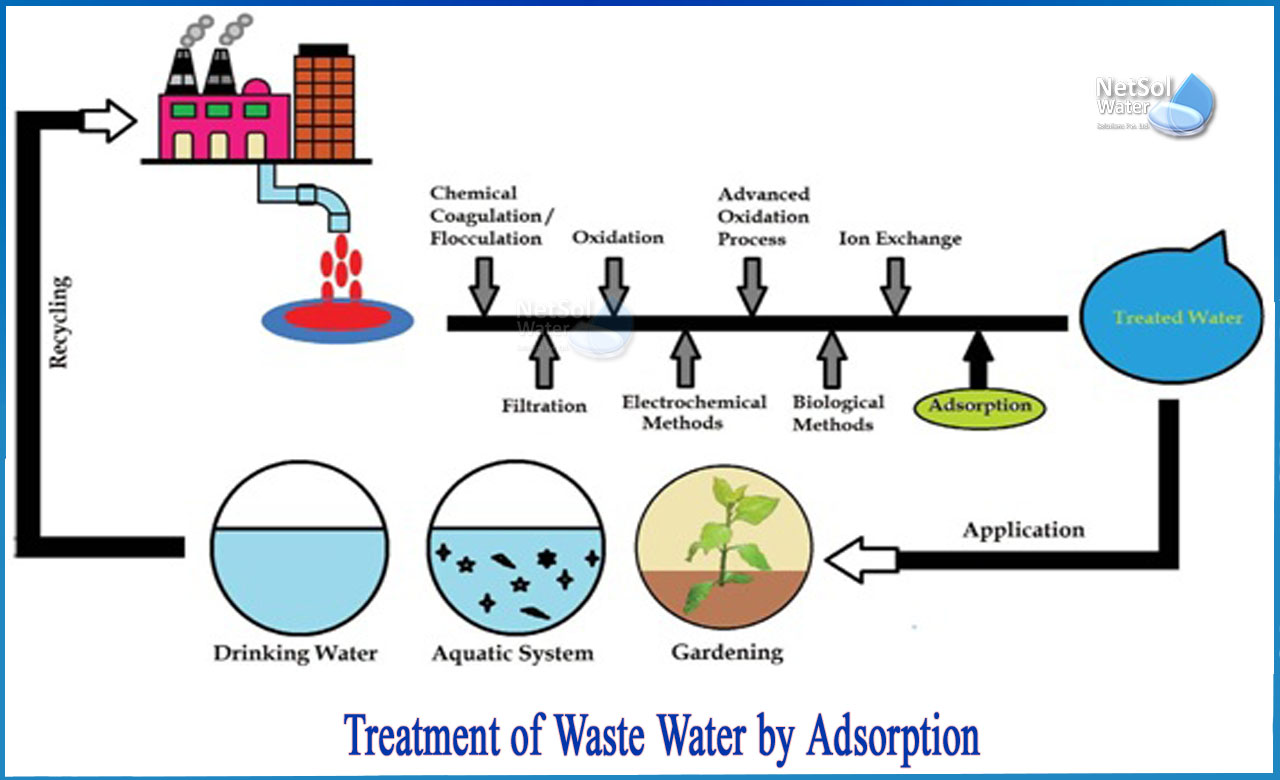
What is adsorption in waste water?
Adsorption with active carbon is frequently used as tertiary purification for the removal of organic micropollutants and COD from wastewater, as well as metals in organic complexes to a lesser extent. The adsorption factor is determined by various groups and compounds in the substances to be removed.
Description of the method and installation
Adsorption is a wastewater purification technique used to remove a variety of compounds from industrial wastewater. Adsorption is most commonly used to remove non-degradable organic compounds from groundwater, drinking water preparation, process water, or as a tertiary cleansing step after biological water purification.
Adsorption occurs when molecules in a liquid bind to the surface of a solid substance. Adsorbents have a large internal surface area that allows for adsorption.
Active carbon is by far the most commonly used adsorbent, and it is especially well-suited to the removal of a polar compounds.
Other adsorbents are employed in specific applications:
1: Zeolites, whether natural or synthetic (alumina-silicate-polymers)
Possess a very homogeneous pore distribution as well as polar bonding sites. Zeolites are far more selective than active carbon
2: Naturally occurring clay minerals
Used to adsorb very polar organic and inorganic matter (ions);
3: Silica gel and aluminum that has been activated
Adsorbents with a high affinity for water that are typically used to remove water from a polar medium.
4: Silicic acid
Wood, charcoal, and coconut can all be used to produce active carbon. Each type has a distinct surface, grain size, and pore diameter. Active carbon is available in powder, granular, and impregnated forms.
Active carbon in powder form is added to aerobic and anaerobic wastewater purification systems, as well as physico-chemical wastewater purification processes. In this case, the added active carbon is removed and treated alongside the resulting sludge.
5: Various other applications
In open or closed filters, active carbon in the form of grains or pellets is commonly used. In most industrial applications, closed filters are used. They are constructed in such a way that the to-be-treated liquid is pumped under pressure through the filter and over the active carbon. Open filters are most commonly used in drinking water applications, where water flows through active carbon beds using gravity.
A typical industrial active carbon is made up of two columns. Both columns have a downward slant. Over time, the carbon becomes saturated, reducing the filter's effectiveness until it no longer adsorbs. Carbon can be thermally regenerated after saturation. This is done in a high-temperature reactivation oven. During this process, the organic compounds that have been adsorbed are destroyed. Following that, the carbon can be redeployed.
To increase the activity of active carbon, it can be chemically impregnated. Impregnated carbon was created specifically to absorb chemical substances that are difficult to absorb with standard activated carbon. For the removal of organic sulphides, ammoniac, and amines, impregnation with COH, K2CO3, H2SO4, and Sulphur is possible.
Adsorption installations that use adsorbents other than activated carbon typically consist of two columns that become saturated over time. Chemicals are used to regenerate zeolites and adsorbents that adsorb inorganic matter (e.g. NaCl solution for zeolites).
Filtration with active carbon
Adsorption with active carbon is frequently used as tertiary purification for the removal of organic micropollutants and COD from wastewater, as well as metals in organic complexes to a lesser extent.
The adsorption factor is determined by various groups and compounds in the substances to be removed.
Here are a few examples of how the technique is used, though this is by no means an exhaustive list:
>Active carbon adsorption is frequently used in soil remediation for groundwater purification, removing BTEX, chlorinated hydrocarbons, and PAH. This technique is especially useful for purifying small volumes or for temporary (short) pumping.
>Active carbon is used in textile distribution to remove difficult-to-degrade compounds such as colorants.
>Active carbon filtration is used in the chemical processing industry to remove toxic substances (pesticides) from partial flows, as well as to keep the biological wastewater purification system from becoming clogged.
>Active carbon adsorption can also be used to remove PER from wastewater generated by the dry cleaning industry.
Other types of adsorbents
Other adsorbents are used at low concentrations or when selectivity is required. For example, zeolites can be used to remove iron, ammonium, nitrate, manganese, or heavy metals.
No comments:
Post a Comment