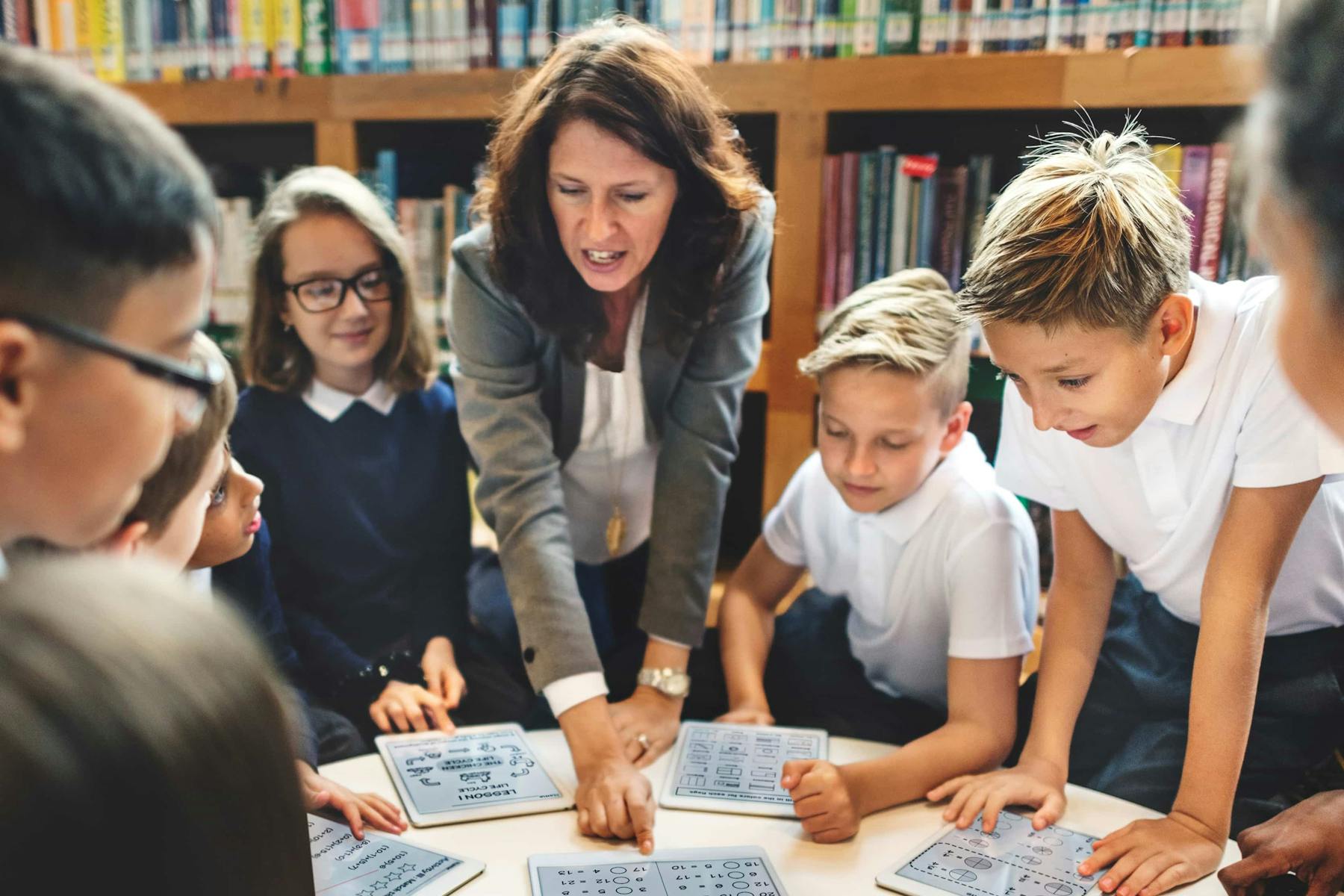
Are you looking for a new way to provide small group instruction with your larger-sized class? Or do you just want something new and exciting in your classroom?
Station rotation may be a great option for you! This classroom management tool is useful whether your students are physically in the classroom or are learning from home.
Many teachers assume that station rotation can only be used in elementary lesson plans, but it can be adapted for every grade level. It helps engage students in the learning process, which is useful no matter what subject or age you are teaching.
This article will outline what the station rotation model is, the various types of stations you can use, and what benefits the station rotation model has. You’ll also find some practical tips for implementing this model in your classroom. Read on to find out more.
What is the station rotation model?
The station rotation model is a series of various learning modalities that students rotate through on a fixed schedule.
Put another way, students spend a set amount of time, like 15 minutes, at each station before rotating to the next one. Each station will focus on a particular skill or concept. Students get hands-on experience trying to solve a puzzle or do an activity, like a word game.
There is a connection between the station rotation model and the blended learning model. Since 2020, schools have been adopting hybrid schedules (largely due to the pandemic) and embracing technology in the classroom.
Some teachers may opt to have one of their stations be an online learning session. This option brings technology into their classroom and blends the learning experience.
Each classroom, teacher and student has different resources and skills. Technology-based stations may be more difficult for some teachers to set up than others. That’s okay! You can do whatever is best for your classroom and students. Blended station rotation is merely one option of many.
Different station rotations for all grade levels
If you teach in a high school classroom, you may be thinking, ‘How can this work for my students?’ While it may not seem quite as obvious how to adopt this method outside of an elementary school classroom, it is still possible.
There are many creative ways to give differentiated instruction that engages students regardless of how advanced they are. This model leans into the idea that one size does not fit all. Station rotation allows you to cater to different learning styles and preferences.
For example, all of your stations can work together to teach one concept. But each station allows the students to experience it in a different way.
The different station rotations can provide visual, auditory and sensory experiences that help all students understand the concept more deeply.
Adjusting the time spent at each station may help make it more age-appropriate for your classroom. Most experts recommend spending about 10-15 minutes per station, but this isn’t a hard and fast rule. You can do whatever works best for your students.
There are three main ways that stations are set up. We’ll share those with you, and hopefully it’ll spark some ideas on how you can use this method in your next lesson plan!
Teacher-led station
This style prioritizes teachers engaging with small groups of students to further explain the lesson and clear up any misunderstandings.
If you have multiple teachers or teaching assistants in your classroom, you may be able to have multiple teacher-led stations that cover different concepts.
If it’s just you teaching in your classroom, a teacher-led station can be just one of your rotations. This station will give you dedicated time to check in with each student and evaluate their level of understanding.
It can also give you an opportunity to discuss a student’s personal application of the lesson to real life. This space allows teachers to build connections with individual students and understand what explanations, support, or models they need to be successful.
Not every approach works for all students, so teacher-led stations give you the feedback you need to personalize your content. It can help you see where you need to adapt the lessons for the variety of learning styles in your learning community.
There are many templates for teacher-led stations online if you need some more ideas or guidance.
Offline station
Offline stations are a time to put the screens down and focus on hands-on collaboration. It also gives students an opportunity to flex their problem-solving skills.
These stations provide learning experiences through books, manipulatives, journals and more. They often encourage students to individually reflect on the lesson or illustrate it in some way.
Students are given quite a bit of agency in this approach. They are allowed the freedom to explore the concept on their own and answer any questions they have. They can further explore certain areas of the topic that interest them.
This agency often improves engagement and motivation over time, which enriches the learning environment of the classroom as a whole.
Examples of this type of station could be a collaborative group project where students design a sustainable city or an individual journal in which students reflect on the story from language arts.
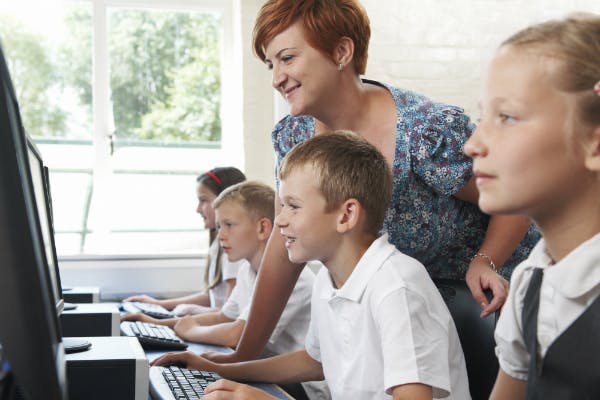
Online station
Online stations are just one way that you might choose to use technology in the classroom.
The biggest benefit to online stations is they allow students to work at their own pace, spending more time on concepts that they don’t understand and breezing through ones that they do.
Teachers are able to provide a more dynamic approach to their content, catering it to meet each student’s needs. Online programs are often driven by individual data with the exercises adapted to a student’s understanding.
Using technology-based stations can also allow group discussions and projects when the class isn’t together in person. Meetings can be carried out via video conferencing or students can message back and forth with ideas.
It’s important that there are safeguards put in place if you choose to use online station rotations. These safeguards will help keep students on task and learning. Some options for this include using timers or setting boundaries for when and where screens are used in the classrooms.
Each student’s familiarity and skills with technology are different. So it’s important to make sure that each student has the tools and support they need to be successful if you choose to use a new form of technology in your lesson plan.
If you have the resources available to you to set up technology-based learning but aren't sure what games to use, don’t worry. There are lots of tips online for picking great learning games. Many of the options are even free!
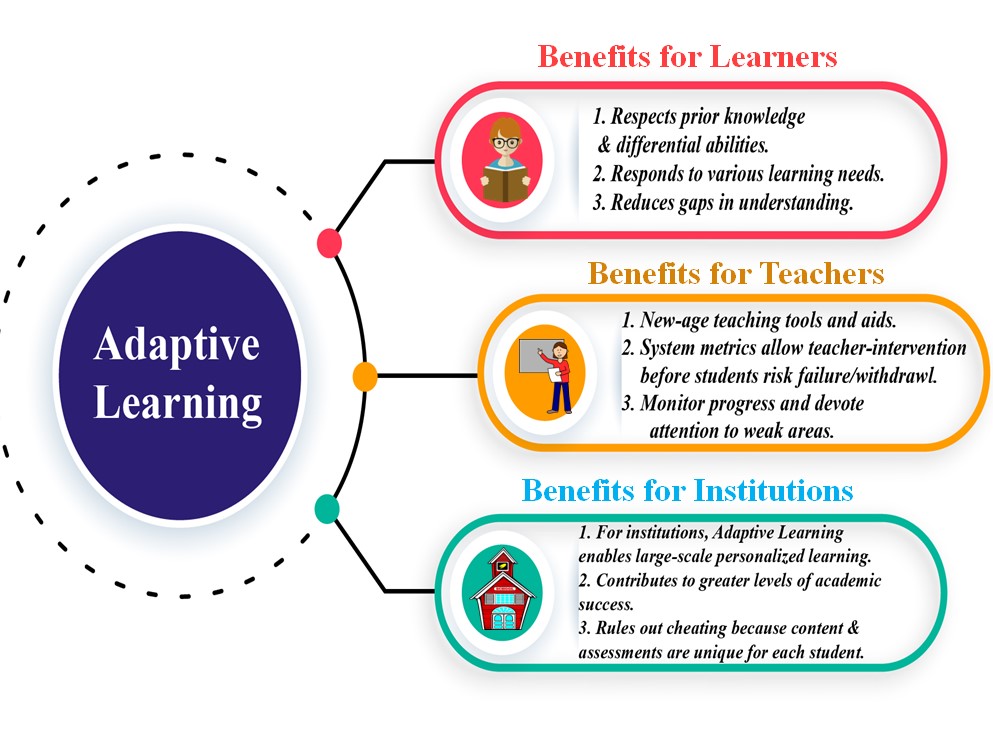
The benefits of the station rotation model
There are various benefits that you may experience after implementing the station rotation model. Each classroom is unique, so it won’t be the same for everyone. But here are a few of the most common benefits.
This model often increases the amount of collaborative learning between students. The ability to collaborate well with others is a skill that will serve students well throughout their educational and vocational journeys. Not to mention, it carries into personal relationships and social skills.
Teachers are also able to personalize their lessons a lot more with the station rotation model. You will be able to focus more intently on individual learners' needs and learning styles.
And in a time when class sizes are continuing to grow, it helps you have more time to focus your attention on smaller groups of students. While other stations are assisting your students in learning independently, you have the ability to check in with every student in your class.
The station rotation models also give students hands-on experience. This time deepens their understanding of the concepts and gets them excited about learning more.
Implementing the station rotation model
Adding the station rotation model to your lesson plan can help your students gain a deeper understanding of the concept while giving you the opportunity to check in with your students. There are many ways to implement the station rotation model, and you can create stations that are individualized to your students.
Another resource that can assist you in personalizing your students’ learning experience is Prodigy. Prodigy is a game-based learning platform that provides standards-aligned, adaptive skill practice in math and English. It also helps you:
- Differentiate instruction for every student
- Engage students with learning that prioritizes motivation
- Unlock insights and identify learning gaps with student reports
- Easily supplement other learning materials and teaching strategies (including using it as a station rotation!)
And the best bit, it's all available at no cost to teachers and schools.