A scrubber is a cleaning installation whose main purpose is to neutralize harmful components in industrial air or waste gas streams. The removal of gas particles causing many problems from the gas stream during the process is necessary before disposing of the gases in the open air.
Traditionally, the term “scrubber” is being referred to pollution control devices which are using liquid to wash unwanted pollutants from a gas stream. Scrubber systems such as chemical scrubbers, gas scrubbers are a diverse group of air pollution control devices. In this article, we will study the scrubber system. Scrubbers remove the unwanted gases and particulate matter from industrial smokestacks before they enter the atmosphere. Here we will have some answers to questions like definition and types of scrubber system. Also, its working will be explained in a simple way.

Definition of Scrubber
Scrubbers are devices to control air pollution and used to remove some particulates and gases from industrial exhaust streams.
Actually, in the scrubber system, the exhaust gas is passed in the column from downside and scrubbing solution/material is sprayed at top. Here Liquid-Gas i.e. wet scrubber or Gas-Solid powder i.e. dry scrubber operation takes place.
Working of Scrubber
A scrubber is a cleaning installation whose main purpose is to neutralize harmful components in industrial air or waste gas streams. The removal of gas particles causing many problems from the gas stream during the process is necessary before disposing of the gases in the open air.
In some cases, the use of a gas scrubber may allow recovering certain raw materials after the treatment. A big advantage is the versatility of a gas scrubber in different areas. It includes the chemical industry, the pharmaceutical industry, and surface treatment.
The installation functions by bringing a gas stream in contact with a washing liquid. Due to this contact, certain gaseous components dissolve and remain in the water.
There is a transfer of the components from the gas phase to the liquid phase. This is the absorption process. The solubility of the elements in the liquid will determine to what extent the gaseous components dissolve into the liquid phase.
Thus it is of great importance to work with the correct fluid being as the absorption agent. Also besides the water, several organic or inorganic washing liquids can also be used for this purpose.
In these cases, certain chemicals or micro-organisms are added to the washing liquid in order to convert or neutralize the dissolved gases.
More strict measures are taken in terms of allowed air pollution. Companies are being encouraged to take the necessary measures about it. Gas scrubbers are essential in industries where employees face exposed to potentially contaminated gases.
When we use a scrubber in an optimal manner, we can achieve a very high removal efficiency of the harmful gas particles. Therefore the fumes released in the outside air are no longer damaging to the environment.
Types of Scrubber
The two main types of scrubbers are wet scrubbers and dry scrubbers.
- Wet Scrubbers
Wet scrubbers force the polluted fumes to pass through a wet limestone slurry which traps sulfur particles. These can be used to control particulate matter less than 10 micrometers as well as inorganic gases such as SO2, H2S, NH3, and various chlorides and fluorides. Wet scrubbers may also be useful to control volatile organic compounds i.e. VOCs.
Condensation scrubbing causes the pollutants to condense so that they can be easily removed. Impingement-plate scrubbers force the emissions up a vertical chamber with water flowing down the sides of the chamber to trap sulfur particles. Coal-fired power plants with scrubbers mostly use a wet scrubber system.
- Dry Scrubbers
Dry scrubbers have an efficiency of more than 90 percent for removing SO2 under the right conditions, but they are limited to small- to medium-sized power plants of about 200 MW. Of the 120 thousand megawatts of power generated from coal-fired power plants with scrubbers.
Also, only 16,200 megawatts come from facilities using a dry scrubber system. There are some advantages of using this technology, including low waste disposal costs and low water consumption. Other contaminants treated by dry scrubbers are polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons i.e. PAHs, HF, HCL, and heavy metals.
Question on Scrubber
Q: How effective are scrubbers?
Ans: Scrubbers are very efficient air pollution control devices, and can remove greater than 95 percent of the SO2 from power plant stack emissions. In fact, SO2 removal efficiencies sometimes are as high as 98 percent to 99 percent. Scrubbers with advanced designs routinely meet targeted efficiencies of more than 95 percent.
A Wet Scrubber is an air pollution control device which uses a liquid to remove contaminants from a gas stream.
The removal process is achieved by bringing the gas stream into contact with the scrubbing liquid, which facilitates mass transfer of the contaminants into the liquid. When the water is recirculated, addition of fresh water is necessary to purge contaminants and replace evaporation losses. Fresh water may be added to the recycle continuously or periodically.
a variety of high-efficiency wet scrubbers for the removal of inorganic gases, odors, fumes, acid fumes, sulfuric acid, chrome, NOx, fine particulate, fine dusts from industrial gas streams, mercury, HCl, Cl2, SO2, and HF.
Applications include a broad range of manufacturing and process industries; semiconductor, metal finishing, and chemical industries generating corrosive fumes and gases.
5 Scrubber design factors are influenced by the type of pollutant being removed: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 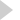 | Packed Bed Height: relates to the required contact time between the pollutant-laden gas stream and the scrubbing liquid to achieve mass transfer. The packed bed height is sized according to the type of pollutant and efficiency requirements. |
| 2 |  | Scrubbing Liquid Type: When scrubbing acidic pollutants, a caustic (e.g. NaOH) may be added to the scrubbing liquid to aid in acid absorption. Likewise, an acid (e.g. H2SO4) may be added to the scrubbing liquid if the pollutant is caustic. |
| 3 |  | Liquid Flow Rate: The flooding factor of the packed bed. |
| 4 |  | Target Gas Velocity: 250 to 450 fpm through a scrubber vessel. Design velocity differs based on the pollutant. |
| 5 |  | Materials of Construction: Chemical compatibility, also cost, are two considerations. |
Tri-Mer’s Wet Scrubber Design:
 | Scrubber body |  |
 | Outlet from the scrubber | |
 | Mist eliminator | |
 | Mist eliminator access door | |
 | Recirculation liquid distribution nozzle system | |
 | Recirculation piping system | |
 | Recirculation pumps: single or redundant, as shown | |
 | (Optional) recirculation system basket strainer for prevention of pump damage and nozzle plugging | |
 | Liquid flow meter | |
 | Packing media: Tri-Packs | |
 | Packing support grid | |
 | Scrubber inlet (round or rectangular) | |
 | Recirculation tank | |
 | Recirculation sump level control system | |
 | Packing removal portal | |
 | Packing fill door |
Vertical Flow:
- Gas flow is counter-current to the liquid flow.
- Smaller footprint required at the expense of increased height requirements.
- Generally, less costly from both capital and operational perspectives.
- Scrubber vessel is round (generally).

Crossflow/Horizontal Flow:
- Gas flow is cross-current (perpendicular) to the liquid flow.
- Sacrifices footprint for height.
- Slightly less efficient due to cross-current flow, although this disadvantage is minimized when treating the more water-soluble acids (e.g. H2SO4, HCl).
- Scrubber vessel is rectangular
What is a Wet Scrubber?
A Wet Scrubber is an emission control device that abates particulate (PM) or gases using a scrubbing liquid. The type of scrubbing liquid used is dependent on the target contaminants that need treatment. The dirty exhaust stream is introduced into the scrubber vessel and interacts with the scrubbing liquid. Here, the contaminated stream undergoes a chemical reaction or becomes captured by the scrubbing liquid before blowdown.
Particulate Dust Scrubbers are wet scrubbers that target particulate matter and comprises both Venturi and Multi-Vane Scrubber systems. These systems are suitable for processes with fine dust or sticky residues since they use liquid to collect the contaminant in a sump for blowdown.
Sub-type of particulate dust scrubbers that integrate a venturi throat into the design to accelerate the process exhaust stream, leading to high removal of particulate matter in batch and continuous-type applications.
Multi-Vane Particulate Scrubbers (MVS)
High-efficiency wet particulate scrubbers that can treat gas streams with moisture and/or high temperatures. They offer higher removal efficiencies using little energy with a relatively small footprint.
These wet scrubbers reliably remove gaseous compounds such as ammonia, chlorine, and sulfuric acid from industrial exhaust streams.
Chemical Gas Scrubbers that typically use sulfuric acid (H2SO4) to neutralize the ammonia.
Chemical gas scrubbers that use an alkaline scrubbing liquid to strip chlorine from your process waste stream.
Chemical Gas scrubbers that use liquid caustic to neutralize sulfur-based substances in your process stream.
No comments:
Post a Comment