The main differentiating point for the sensible heat vs latent heat is that the latent heat is responsible for the change in phase of the substance while the sensible heat is responsible for the change in temperature of the substance.
Latent heat (Non sensible heat):
The amount of heat required for the change in phase of the substance is known as Latent heat.
The latent heat can be classified into three types:
A) Latent heat of fusion/melting:
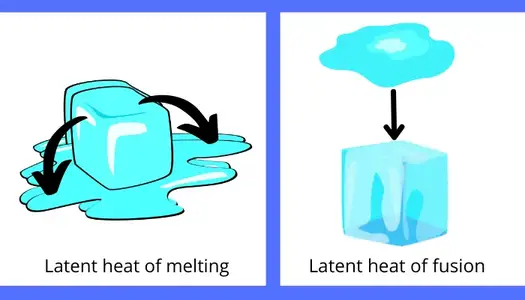
The amount of heat responsible for the change in phase of the substance from solid to liquid or from liquid to solid is known as latent heat of fusion/melting.
Example: The amount of heat required for the melting of the ice is the latent heat of melting and the heat rejected by the water for the formation of the ice is the latent heat of fusion.
B) Latent heat of vaporization/condensation:
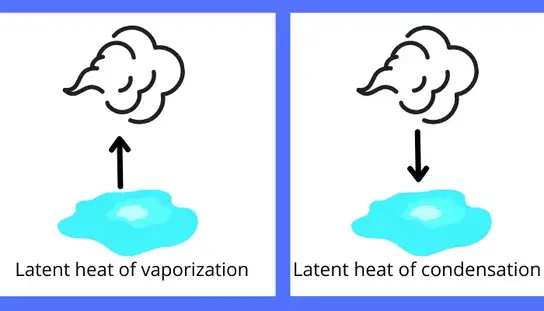
The amount of heat responsible for the change in phase of the substance from liquid to vapor or from vapor to liquid is known as latent heat of vaporization.
Example: The amount of heat required for vaporization of the water is the latent heat of vaporization and the heat rejected by the steam for the condensation is the latent heat of vaporization for the water.
C] Latent heat of sublimation:
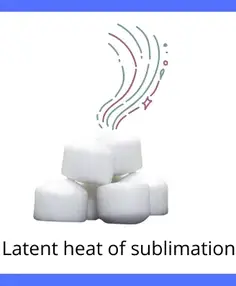
The amount of heat responsible for the change in phase of a substance from solid-state to directly into vapor state is known as latent heat of sublimation.
Example: Sublimation of camphor.
Sensible heat:
The heat which is responsible for the change in temperature of the substance is known as Sensible heat. The sensible heat can be sensed manually because of the rise in the temperature of the object. During the exchange of the sensible heat, the object doesn’t change its phase.
Example: The heat required for the heating or cooling of the water.
Difference between Sensible heat and Latent heat:
| Sr. No. | Latent heat (Non-Sensible heat) | Sensible heat |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Latent heat is not responsible for the raising or lowering of the temperature. | Sensible heat is responsible for the raising or lowering of the temperature. |
| 2 | The latent heat is responsible for the change in phase of the substance (Solid to liquid, liquid to vapor, and vice versa). | The sensible heat is not responsible for the change in the phase of the substance. |
| 3 | During the latent heat transfer, the substance is under phase transition, and the temperature is constant. | During the sensible heat transfer, the temperature of the substance changes without changing the phase of the substance. |
| 4 | Example: Heating or the cooling of the water, etc. | Example: Melting of ice, Vaporization or water, etc. |
No comments:
Post a Comment