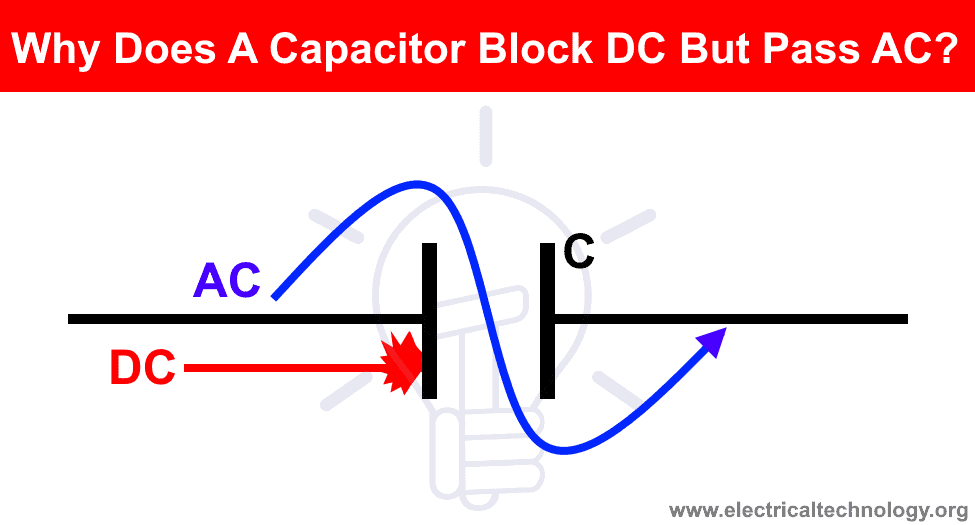
One of the most common question asked by electrical engineering students again and again that’s why do capacitors block DC and allow AC?. To know the exact reason, let’s know what is a capacitor and how it works when connected to DC and then AC supply source.
What is a Capacitor?
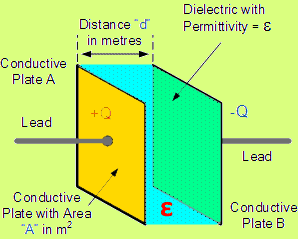
Capacitor (also known as condenser) is a two metal plates device separated by an insulating medium such as foil, laminated paper, air etc. It stores the energy in the form of electrostatic filed and released to the circuit when needed in case of AC. It storage ability is measured in Farad “F” and “µF” or “nF” units are used for small capacitors. Keep in mind that capacitor acts as an open circuit in DC i.e. it only operable at AC voltages.
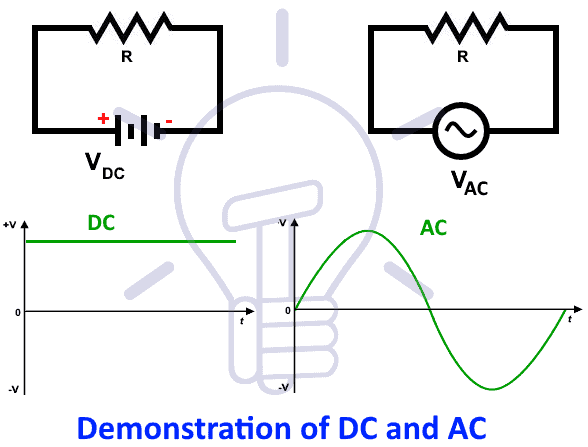
Difference Between AC and DC
DC is a constant value i.e. it doesn’t change the polarity (direction) and magnitude while AC changes its direction and amplitude continuously related to its frequency as shown in fig below.
Now lets connect the capacitor in DC and then AC and see what happens?
Why Does a Capacitor Block DC?
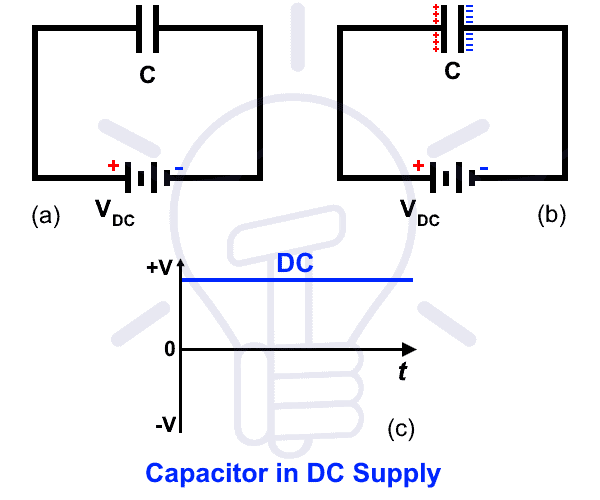
Keep in mind that a capacitor act as a short circuit at initial stage and a fully charged capacitor behave as an open circuit. Capacitors resist a changes in voltage while inductors resist a change in current and acts as a short circuit in DC.
At initial stage when we connect a capacitor to the DC supply, there will a small current of flow will occur until the plates becomes saturated. In other words, the positive terminal of DC supply source will suck the electrons from one terminal and push the electrons to the second terminal until the first plate becomes positively charge and the second one as negatively charged as shown in fig. At this stage, the applied voltage equal to the voltage across capacitor and capacitor plates are saturated and there is no more flow of current. At this stage, capacitor behaves like an open circuit and if we increase the value of applied DC voltage, the capacitor may damage and explode.
Let’s see with a solved example of DC connected capacitor.
We know that there is no frequency i.e. 0Hz frequency in DC supply.
If we put frequency “f = 0″ in the inductive reactance (which is AC resistance in capacitive circuit) formula.
XC = 1 / 2πfC
Putting f = 0
XC = 1 / 2π 0 C
XC = 1/0 = Infinity
It means, theoretically, a capacitor will provide infinite resistant to the flow of current according to its rating. Hence no current flow will occur as current in capacitive circuits are:
I = V / XC
If we put XC as infinity, the value of current would be zero.
I = 0 A
That is the exact reason why a capacitor block DC.
Why Does a Capacitor Pass AC?
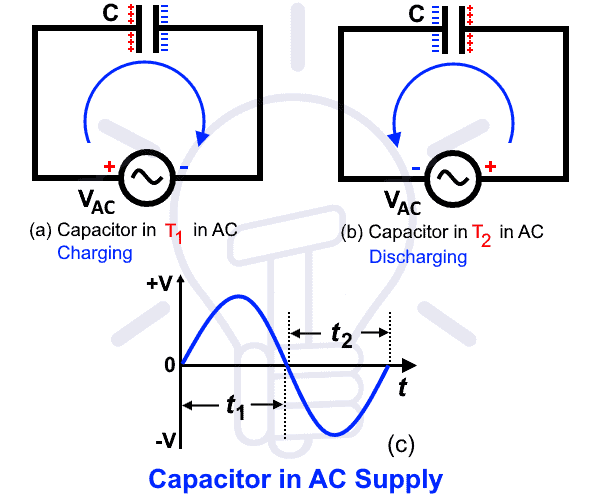
When we connect a capacitor across an AC supply source, it starts charge and discharge continuously due to continuous change in the supply voltage. This is due to changes in AC voltage i.e. AC is positive in the initial cycle for “t = 1” and negative in the second cycle “t = 2” as shown in fig below.
In fig 2(a), same happens like in DC connected capacitor at the initial stage i.e. the positive terminal of source sucks the electrons from the connected plat of the capacitor and pushes back to the second terminal. The first plat becomes positive and the other one is negative due to plenty of electrons. This process is known as charging of a capacitor i.e. it store the energy in the form of electric field.
Charging of a capacitor is given by:
VC = VS (1− e (−τ/RC))
or
VC = VS (1 – e–τ/τ)
Where:
- VC = Voltage across the Capacitor
- VS = Source or Applied Voltage
- e = 2.718 (Exponential i.e the base of the natural logarithm)
- τ = R/C = “tau” time constant in seconds
Now, the polarity of applied voltage is reversed i.e. positive becomes negative and vice versa as shown in fig 2(b). Now the negative source terminal attracted to the holes and pushes back the electrons to the holes in the opposite direction. The process remains continuous and current flows due to the continuous flow of electrons. This process is known as discharging of a capacitor i.e. it restores back the stored energy to the circuit.
The discharging of a capacitor is given by:
VC = VS x e (−τ/RC))
Why Capacitor is rated in DC then?
We know that there are different capacitors with different marking rating on its nameplates i.e. 400VDC or 400VAC. If a capacitor blocks DC, why the rating is mentioned in DC?
Well, Its not means that we can’t use capacitors in DC circuits (you already seen them). The value of DC printed on capacitor nameplates are the maximum value of DC voltage which can be safely connected to it. Keep in mind that it is not the value of charging capacity. Polarized capacitors are mostly used in DC while non-polarized are used in AC circuits.
As a rule of thumb;
- AC marked capacitors can be used on DC.
- DC marked capacitors can’t be used on AC.
Because, the AC voltages shows the RMS value where the peak value of AC is 1.414 times greater than DC.
Applications of Capacitors in DC
- Filters
- Rectifiers (AC to DC conversion)
- Power conditioning
- Coupling Capacitor and Decoupling Capacitor etc.
Applications of Capacitors in AC
- Transformer less power supply
- Split phase induction motors
- Power Factor Correction and Improvement etc.
No comments:
Post a Comment